会添加的吧,会添加的吧?一定会添加的吧!
CF786B Legacy
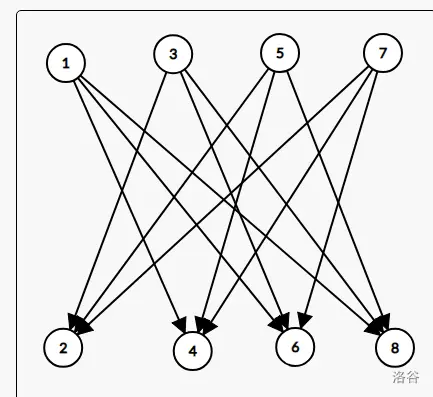
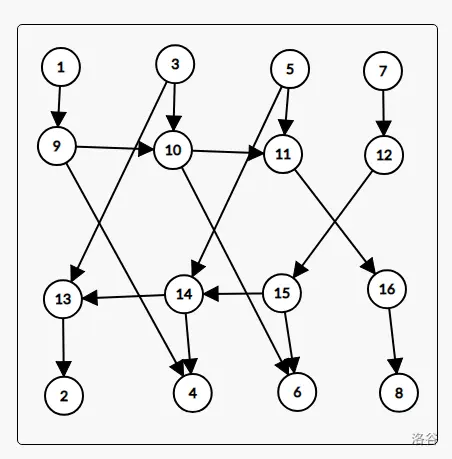
区间向区间连边,我们可以利用线段树的优秀区间特性来进行连边。具体来说,我们建立两颗线段树,一颗专门管入边,一颗管出边入边的树父节点向子节点连边(如果子节点向父节点连边,会导致本来只连向该区间的边通过子节点向父节点连的边连向了更大的区间),同理出边的子节点向父节点连边。父子节点之间的边,边权为 0 。
总边复杂度大约在O ( m log n ) O(m \log n) O ( m log n )
例如上图,本题代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long #define ls (p<<1) #define rs (p<<1|1) #define pir pair<int,int> using namespace std;constexpr int MN=4e6 +15 ,K=6e5 ;struct Edge { int v,w; }; int n,q,s,dis[MN],pos[MN];vector<Edge> adj[MN]; bool vis[MN];inline void add (int u,int v,int w) adj[u].push_back ({v,w}); } void build (int p,int l,int r) if (l==r){ pos[l]=p; return ; } add (p,ls,0 ); add (p,rs,0 ); add (ls+K,p+K,0 ); add (rs+K,p+K,0 ); int mid=(l+r)>>1 ; build (ls,l,mid); build (rs,mid+1 ,r); } void updatetoqj (int p,int l,int r,int fl,int fr,int u,int w) if (l>=fl&&r<=fr){ add (u+K,p,w); return ; } int mid=(l+r)>>1 ; if (mid>=fl) updatetoqj (ls,l,mid,fl,fr,u,w); if (mid<fr) updatetoqj (rs,mid+1 ,r,fl,fr,u,w); } void updatefromqj (int p,int l,int r,int fl,int fr,int u,int w) if (l>=fl&&r<=fr){ add (p+K,u,w); return ; } int mid=(l+r)>>1 ; if (mid>=fl) updatefromqj (ls,l,mid,fl,fr,u,w); if (mid<fr) updatefromqj (rs,mid+1 ,r,fl,fr,u,w); } void dijk (int begin) memset (dis,0x3f ,sizeof (dis)); priority_queue<pir,vector<pir>,greater<pir>>q; q.push (pir (0 ,begin)); dis[begin]=0 ; while (!q.empty ()){ int u=q.top ().second; q.pop (); if (vis[u]) continue ; vis[u]=1 ; for (auto e:adj[u]){ int v=e.v,w=e.w; if (dis[v]>w+dis[u]){ dis[v]=w+dis[u]; if (!vis[v]) q.push (pir (dis[v],v)); } } } } signed main () cin>>n>>q>>s; build (1 ,1 ,n); for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ add (pos[i],pos[i]+K,0 ); add (pos[i]+K,pos[i],0 ); } while (q--){ int op,u,fl,fr,w,v; cin>>op; if (op==1 ){ cin>>u>>v>>w; add (pos[u]+K,pos[v],w); }else if (op==2 ){ cin>>u>>fl>>fr>>w; updatetoqj (1 ,1 ,n,fl,fr,pos[u],w); }else if (op==3 ){ cin>>u>>fl>>fr>>w; updatefromqj (1 ,1 ,n,fl,fr,pos[u],w); } } dijk (pos[s]+K); for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ cout<<(dis[pos[i]]<0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f ?dis[pos[i]]:-1 )<<" " ; } return 0 ; }
可以用于连边区间序列的前后缀或树上根链的情况。
这一部分优化的是一个点向一整个前缀或后缀连边,暴力连边数可达到惊人的O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O ( n 2 )
我们通过对于每一个节点i i i p r e i , s u f i pre_{i},suf_{i} p r e i , s u f i i → p r e i , p r e i − 1 → p r e i i \to pre_{i},pre_{i-1} \to pre_{i} i → p r e i , p r e i − 1 → p r e i s u f suf s u f
对于树上根链,直接建内向树,连根链末尾即可。
Luogu-P6378 PA 2010 Riddle
2-sat 加优化建图:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int MN=8e6 +15 ;int n,m,k,dfn[MN],low[MN],vdcc[MN],tot,dcc; vector<int > adj[MN],gp[MN]; bool vis[MN];int s[MN],top;void tarjan (int u) low[u]=dfn[u]=++tot; s[++top]=u; vis[u]=1 ; for (auto v:adj[u]){ if (!dfn[v]){ tarjan (v); low[u]=min (low[u],low[v]); }else if (vis[v]){ low[u]=min (low[u],dfn[v]); } } if (low[u]==dfn[u]){ dcc++; int p; do { p=s[top--]; vdcc[p]=dcc; vis[p]=0 ; } while (p!=u); } } int main () cin>>n>>m>>k; for (int i=1 ;i<=m;i++){ int u,v; cin>>u>>v; int fu=u+n,fv=v+n; adj[fu].push_back (v); adj[fv].push_back (u); } for (int i=1 ;i<=k;i++){ int num; cin>>num; for (int j=1 ;j<=num;j++){ int p; cin>>p; gp[i].push_back (p); adj[p].push_back (p+2 *n); adj[p+3 *n].push_back (p+n); } for (int j=1 ;j<gp[i].size ();j++){ int d1=gp[i][j-1 ],d2=gp[i][j]; adj[d1+2 *n].push_back (d2+2 *n); adj[d2+3 *n].push_back (d1+3 *n); adj[d1+2 *n].push_back (d2+n); adj[d2].push_back (d1+3 *n); } } for (int i=1 ;i<=n*4 ;i++){ if (!dfn[i]) tarjan (i); } for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ if (vdcc[i]==vdcc[i+n] || vdcc[i+2 *n]==vdcc[i+3 *n]){ cout<<"NIE" ; return 0 ; } } cout<<"TAK" ; return 0 ; }
P3783 [SDOI2017] 天才黑客 - 洛谷
首先这个字典树的边权没有任何卵用,因为题目中已经给出边上的d i d_{i} d i
其次这个题一眼最短时间,说人话就是最短路,考虑 Dijkstra 求最短路,因为这里 SPFA 显然已死(你真的要卡O ( n m ) O(nm) O ( n m )
w ( u , v ) = c ( u , v ) + LCP ( d n o w , d i ) w_{(u,v)} = c_{(u,v)} + \operatorname{LCP}(d_{now}, d_{i}) w ( u , v ) = c ( u , v ) + L C P ( d n o w , d i )
不难注意到题目中慷慨的给我们了字典树,根据字典树上的性质,任意两个点之间的 LCA 节点的深度大小就是这两点的所构成字符串的最长公共前缀长度,那么边权转化为:
w ( u , v ) = c ( u , v ) + d e p { LCA ( d n o w , d i } w_{(u,v)} = c_{(u,v)} + dep\left\{\operatorname{LCA}(d_{now}, d_{i}\right\} w ( u , v ) = c ( u , v ) + d e p { L C A ( d n o w , d i }
但是这里面有一个棘手的地方就是这个d n o w d_{now} d n o w d n o w d_now d n o w i n → o u t in \to out i n → o u t c e c_{e} c e d e p { LCA ( d ( u , v ) , d ( v , t ) ) } dep\left\{ \operatorname{LCA}(d_{(u,v)},d_{(v,t)}) \right\} d e p { L C A ( d ( u , v ) , d ( v , t ) ) }
注意到节点1 1 1 1 → a 1 \to a 1 → a S S S S → a S \to a S → a 0 0 0
让后输出最短路长度的时候,答案即为min b e = i d i s o u t \min\limits_{b_{e}=i} dis_{out} b e = i min d i s o u t
写完交上去,恭喜你 MLE+TLE。为什么?因为边数最高可到达O ( m 2 ) O(m^2) O ( m 2 )
首先原来的i n → o u t in \to out i n → o u t S = { d i ∣ b i = u , a i = u } S=\left\{ d_{i}| b_{i}=u,a_{i}=u \right\} S = { d i ∣ b i = u , a i = u } S S S S S S O ( ∣ S ∣ ) O(|S|) O ( ∣ S ∣ ) ∑ u ∣ S u ∣ = m \sum\limits_{u} |S_u|=m u ∑ ∣ S u ∣ = m O ( m ) O(m) O ( m )
我们考虑把 LCA 这个点拿出来建虚点,在子树中的节点连一个 LCA 的虚点,让后在从这个虚点连向另外一个虚点,让后在利用虚树进行建边,但是这样边数是O ( n ) O(n) O ( n ) O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O ( n 2 )
注意到,我们实际上连边都是在子树中的节点连一个 LCA 的虚点,让后在从这个虚点连向另外一个虚点,考虑这个怎么优化。子树的性质,DFN连续 。那么,问题转化为 DFS 序上的区间向点连边,点向另外一个连续区间连边,这是什么,线段树优化建图啊!让后就做完了,时间复杂度因为连边是O ( log n ) O(\log n) O ( log n ) O ( n log 2 m ) O(n \log^2 m) O ( n log 2 m )
能不能再给力一点啊?
可以的!上述过程我们是在暴力枚举 LCA 的,事实上,如果两点间连了一堆的边,但是只有代价最小的边是有用的 ,剩下都是没太大啥用的,连了也不影响。
我们先把S S S [ 1 , i ] [1,i] [ 1 , i ] [ i + 1 , t ] [i+1,t] [ i + 1 , t ] [ i + 1 , t ] [i+1,t] [ i + 1 , t ] [ 1 , i ] [1,i] [ 1 , i ] t = ∣ S ∣ t=|S| t = ∣ S ∣ min x , y d e p [ lca ( x , y ) ] \min_{x,y} dep[ \operatorname{lca}(x,y)] min x , y d e p [ l c a ( x , y ) ] O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 ) O ( n log m ) O(n \log m) O ( n log m )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long #define pir pair<int,int> using namespace std;constexpr int MN=1e6 +15 ,MLOG=20 ;struct Edge { int v,w; }; struct EDGE { int a,b,c,d; }e[MN]; int n,m,K,S,ans[MN],hlca[MN],ntot,prein[MN],preout[MN],sufin[MN],sufout[MN];vector<int > out[MN],in[MN]; vector<Edge> adj[MN]; vector<pir> vt; namespace Trie{ vector<int > g[MN]; int fa[MN][30 ],dep[MN],dfn[MN],dfntot; void triedfs (int u,int pre) dfn[u]=++dfntot; fa[u][0 ]=pre; dep[u]=dep[pre]+1 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=MLOG;i++){ fa[u][i]=fa[fa[u][i-1 ]][i-1 ]; } for (auto v:g[u]){ triedfs (v,u); } } int lca (int x,int y) if (dep[x]>dep[y]) swap (x,y); for (int i=MLOG;i>=0 ;i--){ if (dep[fa[y][i]]>=dep[x]) y=fa[y][i]; } if (x==y) return x; for (int k=MLOG;k>=0 ;k--){ if (fa[x][k]!=fa[y][k]){ x=fa[x][k],y=fa[y][k]; } } return fa[x][0 ]; } }using namespace Trie; namespace Dijkstra{ int dis[MN]; bool vis[MN]; void dijk (int st) memset (dis,0x3f ,sizeof (dis)); memset (vis,0 ,sizeof (vis)); priority_queue<pir,vector<pir>,greater<pir>> q; dis[st]=0 ; q.push (pir (0 ,st)); while (!q.empty ()){ int u=q.top ().second; q.pop (); if (vis[u]) continue ; vis[u]=1 ; for (auto e:adj[u]){ int v=e.v; if (dis[v]>dis[u]+e.w){ dis[v]=dis[u]+e.w; q.push (pir (dis[v],v)); } } } } }using namespace Dijkstra; bool cmp (pir x,pir y) return dfn[x.first]<dfn[y.first]; } void clear () S=MN-3 ; ntot=dfntot=0 ; memset (dfn,0 ,sizeof (dfn)); memset (dep,0 ,sizeof (dep)); memset (fa,0 ,sizeof (fa)); for (int i=0 ;i<MN;i++){ in[i].clear (); out[i].clear (); g[i].clear (); adj[i].clear (); } } void solve () cin>>n>>m>>K; clear (); ntot=m<<1 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=m;i++){ cin>>e[i].a>>e[i].b>>e[i].c>>e[i].d; out[e[i].a].push_back (i); in[e[i].b].push_back (i); } for (int i=1 ;i<K;i++){ int u,v,w; cin>>u>>v>>w; g[u].push_back (v); } triedfs (1 ,0 ); for (int i=1 ;i<=m;i++){ adj[i].push_back ({i+m,e[i].c}); if (e[i].a==1 ) adj[S].push_back ({i,0 }); } for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ vt.clear (); for (auto p:in[i]) vt.push_back (pir (e[p].d,p+m)); for (auto p:out[i]) vt.push_back (pir (e[p].d,p)); sort (vt.begin (),vt.end (),cmp); for (int j=0 ;j<vt.size ();j++){ prein[j]=++ntot; preout[j]=++ntot; sufin[j]=++ntot; sufout[j]=++ntot; } for (int j=0 ;j+1 <vt.size ();j++){ hlca[j]=lca (vt[j].first,vt[j+1 ].first); adj[prein[j+1 ]].push_back ({prein[j],0 }); adj[preout[j]].push_back ({preout[j+1 ],0 }); adj[sufin[j]].push_back ({sufin[j+1 ],0 }); adj[sufout[j+1 ]].push_back ({sufout[j],0 }); } for (int j=0 ;j<vt.size ();j++){ if (vt[j].second<=m){ adj[sufin[j]].push_back ({vt[j].second,0 }); adj[prein[j]].push_back ({vt[j].second,0 }); } else { adj[vt[j].second].push_back ({sufout[j],0 }); adj[vt[j].second].push_back ({preout[j],0 }); } } for (int j=0 ;j+1 <vt.size ();j++){ adj[sufout[j+1 ]].push_back ({prein[j], dep[hlca[j]]-1 }); adj[preout[j]].push_back ({sufin[j+1 ], dep[hlca[j]]-1 }); } } dijk (S); memset (ans,0x3f ,sizeof (ans)); for (int i=1 ;i<=m;i++){ ans[e[i].b]=min (ans[e[i].b],dis[i+m]); } for (int i=2 ;i<=n;i++) cout<<ans[i]<<'\n' ; } signed main () int T; cin>>T; while (T--){ solve (); } return 0 ; }
P5284 [十二省联考2019]字符串问题
当然是 SAM 做法啦,首先为了求前缀信息直接对反串求后缀自动机。
不难注意到这个支配关系很想一个图中的边,我们思考能不能进行图论建模,但是前缀全部建图是很难受的,但是一个性质,link 树上的祖先在反串上都是它的前缀。
我们记录一下反串每一个位置在后缀自动机上的位置,然后在 link 树上倍增上去找s [ l , r ] s[l,r] s [ l , r ] 子串长度 为第一关键字,是否为 A 类串 为第二关键字排序,然后依次连边。让后把后缀自动机父亲结点挂下来的结点向当前结点连一条边。
然后问题就是在 DAG 上求最长路!
其实就是综合利用 link 树上的祖先在反串上都是它的前缀的特性。
大约是O ( T n log n ) O(Tn \log n) O ( T n log n )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;constexpr int MN=1e6 +15 ;int n,na,nb,m,in[MN],tot,dis[MN],a[MN],b[MN],last[MN],fa[MN],pre[31 ][MN],pos[MN];long long ans;bool isa[MN];string s; vector<int > adj[MN],g[MN]; struct SAM { int nxt[MN][26 ],len[MN],stot,lst; void init () for (int i=0 ;i<=stot;i++){ fa[i]=len[i]=0 ; for (int j=0 ;j<=30 ;j++) pre[j][i]=0 ; memset (nxt[i],0 ,sizeof (nxt[i])); } stot=lst=1 ; } void expand (int c) int cur=++stot; len[cur]=len[lst]+1 ; int p=lst; while (p&&!nxt[p][c]) nxt[p][c]=cur,p=fa[p]; if (!p){ fa[cur]=1 ; }else { int q=nxt[p][c]; if (len[q]==len[p]+1 ){ fa[cur]=q; }else { int nq=++stot; len[nq]=len[p]+1 ; fa[nq]=fa[q]; memcpy (nxt[nq],nxt[q],sizeof (nxt[q])); fa[q]=fa[cur]=nq; while (p&&nxt[p][c]==q){ nxt[p][c]=nq; p=fa[p]; } } } lst=cur; } void initpre () for (int i=1 ;i<=stot;i++) pre[0 ][i]=fa[i]; for (int i=1 ;i<=30 ;i++){ for (int j=2 ;j<=stot;j++){ pre[i][j]=pre[i-1 ][pre[i-1 ][j]]; } } } }sam; bool cmp (int x,int y) if (sam.len[x]==sam.len[y]){ return isa[x]>isa[y]; } return sam.len[x]>sam.len[y]; } void init () sam.init (); for (int i=1 ;i<=tot;i++) in[i]=dis[i]=isa[i]=pos[i]=0 ,g[i].clear (),adj[i].clear (); ans=0 ; } int toposort () queue<int > q; for (int i=1 ;i<=tot;i++) if (!in[i]) q.push (i); while (!q.empty ()){ int u=q.front (); q.pop (); ans=max (ans,1ll *dis[u]+sam.len[u]); for (auto v:adj[u]){ dis[v]=max (dis[v],dis[u]+sam.len[u]); in[v]--; if (!in[v]){ q.push (v); } } } bool flag=0 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=tot;i++){ if (in[i]) flag=1 ; } if (flag) return -1 ; return ans; } void solve () init (); cin>>s; n=s.length (); s=" " +s; for (int i=n;i>=1 ;i--){ sam.expand (s[i]-'a' ); pos[i]=sam.lst; } sam.initpre (); cin>>na; tot=sam.stot; for (int i=1 ;i<=na;i++){ int l,r; cin>>l>>r; int lenn=r-l+1 ,p=pos[r]; for (int i=30 ;i>=0 ;i--){ if (pre[i][p]&&sam.len[pre[i][p]]>=lenn) p=pre[i][p]; } isa[++tot]=1 ; sam.len[tot]=lenn; g[p].push_back (tot); a[i]=tot; } cin>>nb; for (int i=1 ;i<=nb;i++){ int l,r; cin>>l>>r; int lenn=r-l+1 ,p=pos[l]; for (int i=30 ;i>=0 ;i--){ if (pre[i][p]&&sam.len[pre[i][p]]>=lenn) p=pre[i][p]; } isa[++tot]=0 ; sam.len[tot]=lenn; g[p].push_back (tot); b[i]=tot; } for (int i=2 ;i<=sam.stot;i++) sort (g[i].begin (),g[i].end (),cmp); for (int i=1 ;i<=sam.stot;i++){ int lst=i; for (int j=g[i].size ()-1 ;j>=0 ;j--){ adj[lst].push_back (g[i][j]); in[g[i][j]]++; if (!isa[g[i][j]]) lst=g[i][j]; } last[i]=lst; } for (int i=2 ;i<=sam.stot;i++){ adj[last[fa[i]]].push_back (i); in[i]++; } for (int i=1 ;i<=tot;i++){ if (!isa[i]) sam.len[i]=0 ; } cin>>m; for (int i=1 ;i<=m;i++){ int x,y; cin>>x>>y; adj[a[x]].push_back (b[y]); in[b[y]]++; } cout<<toposort ()<<'\n' ; } signed main () int T; cin>>T; while (T--){ solve (); } return 0 ; }
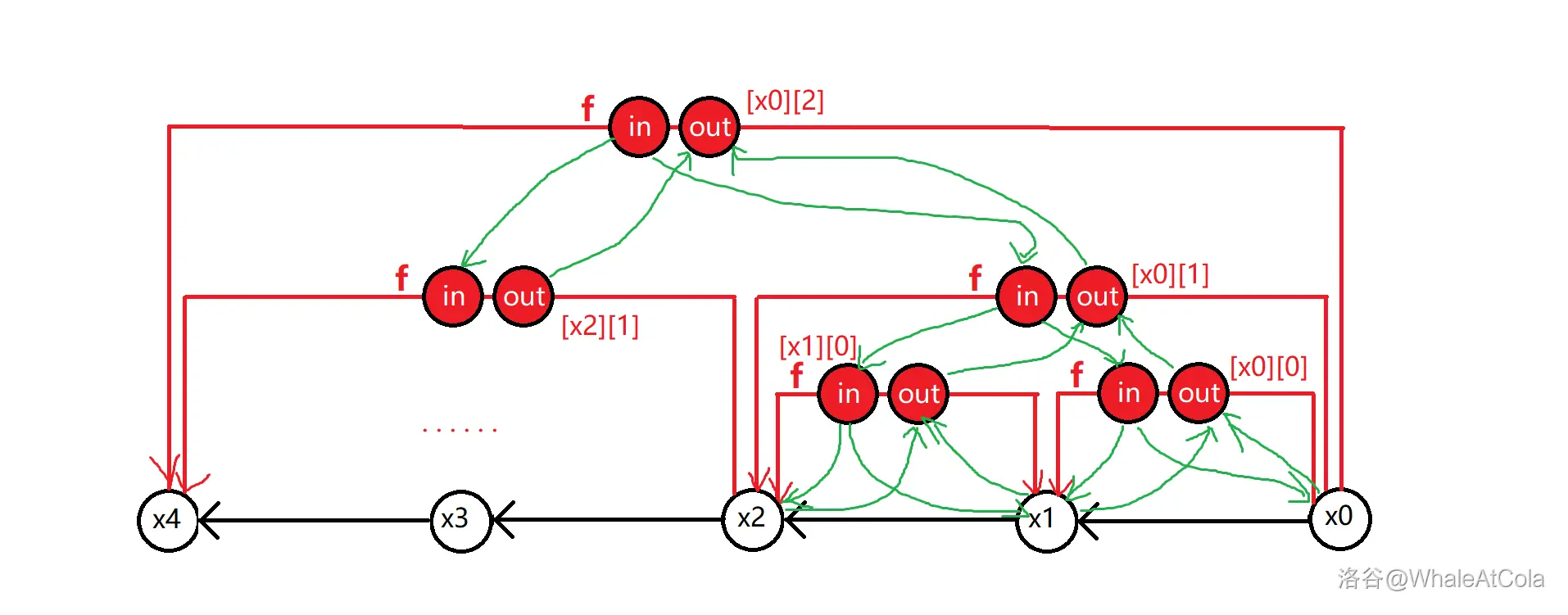
区间向区间连边,可以转化为区间向虚点连边,再由虚点向区间连边。
和线段树建图极其相似,但是不同的是我们这里搬到了书上,我们同样要建出两个树,一个是出边树,一个是入边树,让后我们通过倍增求 LCA 的方法来建立:
每一次我们让[ u 1 , v 1 ] → [ u 2 , v 2 ] [u_1,v_{1}] \to [u_{2},v_{2}] [ u 1 , v 1 ] → [ u 2 , v 2 ] [ u 1 , v 1 ] → o u t [ u 1 , v 1 ] [u_{1},v_{1}] \to out_{[u_{1},v_{1}]} [ u 1 , v 1 ] → o u t [ u 1 , v 1 ] [ u 2 , v 2 ] → i n [ u 2 , v 2 ] [u_{2},v_{2}] \to in_{[u_{2},v_{2}]} [ u 2 , v 2 ] → i n [ u 2 , v 2 ] o u t [ u 1 , v 1 ] → i n [ u 2 , v 2 ] out_{[u_1,v_{1]}\to}in_{[u_{2},v_{2}]} o u t [ u 1 , v 1 ] → i n [ u 2 , v 2 ]
时间复杂度在O ( n log 2 n ) O(n \log^2 n) O ( n log 2 n )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define pir pair<int,int> using namespace std;constexpr int MN=1e7 +15 ;constexpr int INF=0x3f3f3f3f ;struct Query { int u1,v1,u2,v2,w; }qry[MN]; int n,m,st,qtot,dis[MN],pre[MN];bool vis[MN];vector<pir> adj[MN],g[MN]; namespace Tree{ int dep[MN],fa[MN][20 ],dtot; int in[MN][20 ],out[MN][20 ]; void dfs (int u,int pre) dep[u]=dep[pre]+1 ; fa[u][0 ]=pre; in[u][0 ]=++dtot; adj[dtot].push_back ({u,0 }); adj[dtot].push_back ({pre,0 }); out[u][0 ]=++dtot; adj[u].push_back ({dtot,0 }); adj[pre].push_back ({dtot,0 }); for (int j=0 ;j<__lg(n);j++){ fa[u][j+1 ]=fa[fa[u][j]][j]; in[u][j+1 ]=++dtot; adj[dtot].push_back ({in[u][j],0 }); adj[dtot].push_back ({in[fa[u][j]][j],0 }); out[u][j+1 ]=++dtot; adj[out[u][j]].push_back ({dtot,0 }); adj[out[fa[u][j]][j]].push_back ({dtot,0 }); } for (auto e:g[u]){ int v=e.first; if (v==pre) continue ; dfs (v,u); } } void lca1 (int x,int y,int k) if (dep[x]<dep[y]) swap (x,y); adj[y].push_back ({k,0 }); for (int i=__lg(n);i>=0 ;i--){ if (dep[fa[x][i]]>=dep[y]){ adj[out[x][i]].push_back ({k,0 }); x=fa[x][i]; } } if (x==y) return ; for (int i=__lg(n);i>=0 ;i--){ if (fa[x][i]!=fa[y][i]){ adj[out[x][i]].push_back ({k,0 }); adj[out[y][i]].push_back ({k,0 }); x=fa[x][i]; y=fa[y][i]; } } adj[out[x][0 ]].push_back ({k,0 }); } void lca2 (int x,int y,int k) if (dep[x]<dep[y]) swap (x,y); adj[k].push_back ({y,0 }); for (int i=__lg(n);i>=0 ;i--){ if (dep[fa[x][i]]>=dep[y]){ adj[k].push_back ({in[x][i],0 }); x=fa[x][i]; } } if (x==y) return ; for (int i=__lg(n);i>=0 ;i--){ if (fa[x][i]!=fa[y][i]){ adj[k].push_back ({in[x][i],0 }); adj[k].push_back ({in[y][i],0 }); x=fa[x][i]; y=fa[y][i]; } } adj[k].push_back ({in[x][0 ],0 }); } }using namespace Tree; int root (int x) return pre[x]==x?x:pre[x]=root (pre[x]); } void dijk (int st) priority_queue<pir,vector<pir>,greater<pir>> q; memset (dis,0x3f ,sizeof (dis)); dis[st]=0 ; q.push ({0 ,st}); while (!q.empty ()){ int u=q.top ().second; q.pop (); if (vis[u]) continue ; vis[u]=1 ; for (auto e:adj[u]){ int v=e.first,w=e.second; if (dis[v]>dis[u]+w){ dis[v]=dis[u]+w; q.push ({dis[v],v}); } } } } int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); cin>>n>>m>>st; dtot=n; for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++) pre[i]=i; while (m--){ int op,u1,v1,u2,v2,w; cin>>op; if (op==1 ){ cin>>u1>>v1>>u2>>v2>>w; if (root (u1)!=root (v1)||root (u2)!=root (v2)) continue ; qry[++qtot]={u1,v1,u2,v2,w}; }else { cin>>u1>>v1>>w; int ru=root (u1),rv=root (v1); if (ru==rv) continue ; g[u1].push_back ({v1,w}); g[v1].push_back ({u1,w}); adj[u1].push_back ({v1,w}); adj[v1].push_back ({u1,w}); pre[rv]=ru; } } for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++) if (!dep[i]) dfs (i,0 ); for (int i=1 ;i<=qtot;i++){ lca1 (qry[i].u1,qry[i].v1,++dtot); lca2 (qry[i].u2,qry[i].v2,++dtot); adj[dtot-1 ].push_back ({dtot,qry[i].w}); } dijk (st); for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++) cout<<(dis[i]==INF?-1 :dis[i])<<" " ; return 0 ; }
区间向区间连边,可以转化为区间向虚点连边,再由虚点向区间连边。
这个话还是比较管用的,这样复杂度可以大大降低。
但是我题丢了,所以只能放一句话 www。